-
 Open Hours: Mon- Sat 10:00 am - 06:30pm
Open Hours: Mon- Sat 10:00 am - 06:30pm
Calcitonin Nasal Spray Manufacturer & Supplier | PCD Franchise in India
- Home
- MIX PRODUCTS
- Calcitonin Nasal Spray
Hydroxyprogestron Caproate 250mg Injection
March 3, 2023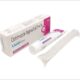
Clotrimazole Vaginal Gel
March 3, 2023
Calcitonin Nasal Spray
₹1,800.00
KOOCAL
SKU: 59c3a01b4a40
Category: MIX PRODUCTS

Description
Calcitonin Nasal Spray: Osteoporosis, a disorder marked by weakening bones, is treated using calcitonin nasal spray. It includes synthetic calcitonin, a hormone that controls the body’s calcium levels. It helps prevent bone deterioration when provided orally, lowering the risk of fractures and boosting bone density. The spray is often applied every day, and because it is applied directly to the nasal membranes, it quickly enters the bloodstream. However, as of my most recent update in September 2021, it’s crucial to adhere to the most recent medical recommendations and seek professional advice before utilizing any medications.
Benefits of Using Calcitonin Nasal Spray
- Treats osteoporosis: Assists those who have the condition in reducing bone loss and fractures.
- Increased bone mass improves bone strength and resilience while increasing bone density.
- Easy application: Nasal spray is simple to use and offers quick application.
- Targeted absorption: Direct nasal membrane absorption that produces quick systemic effects.
- Lessened negative effects are generally well-tolerated and less likely to cause stomach problems than oral options.
How to Use Calcitonin Nasal Spray
- Go over the directions: Read the instructions for using the product that the manufacturer and your healthcare provider have provided.
- Prime the spray: To guarantee correct dosing, pump the spray a few times before using it for the first time.
- To administer the medication, tilt your head slightly forward, place the nozzle in one nostril, and then close the other.
- How to administer the dose: Press the pump to release the drug while taking a gentle nasal breath.
- Use different nostrils: Give the subsequent dose through the different nostrils. Do not blow your nose right after application.
How Does Calcitonin Nasal Spray Works
- Synthetic calcitonin mimics natural hormones: Synthetic calcitonin mimics natural hormones that control calcium metabolism in the body.
- Prevents bone deterioration: It lessens the activity of osteoclasts, which are the cells in charge of destroying the bone structure.
- Promotes osteoblasts’ production of new bone tissue by decreasing bone resorption.
- Decreases fracture risk: Bones with increased strength and density are less likely to fracture.
- Nasal absorption: Easy nasal spray application enables quick bloodstream absorption for systemic effects.
Precautions While Using Calcitonin Nasal Spray
- Obey dosing instructions: Strictly adhere to the dosage and frequency recommended by your healthcare provider.
- Maintain a clear nasal passageway and refrain from using the spray if you have a sinus infection or irritant.
- Keep an eye on side effects: Inform your doctor of any unexpected reactions, such as allergy symptoms or nose congestion.
- Blood calcium levels should be regularly checked to make sure they stay within the usual range.
- pregnant and breastfeeding: Before using during pregnancy or while breastfeeding, speak with your doctor to determine any potential hazards.
Side Effects of Using Calcitonin Nasal Spray
- Nasal irritation: This frequent side effect can be uncomfortable or lead to minor nosebleeds.
- Allergic reactions: Although uncommon, they might cause a rash, itching, or breathing problems.
- Facial flushing: A brief redness or warmth in the face is possible for certain individuals.
- Nausea: Occasional stomach upset that typically goes away with time.
- Nasal modifications: Prolonged use may cause nasal dryness, congestion, or alterations in smell.
Additional information
| PACKING | |
|---|---|
| Composition | Calcitonin Salmon 2200 I.U Nasal Solution USP(30 Metered Doses) |